
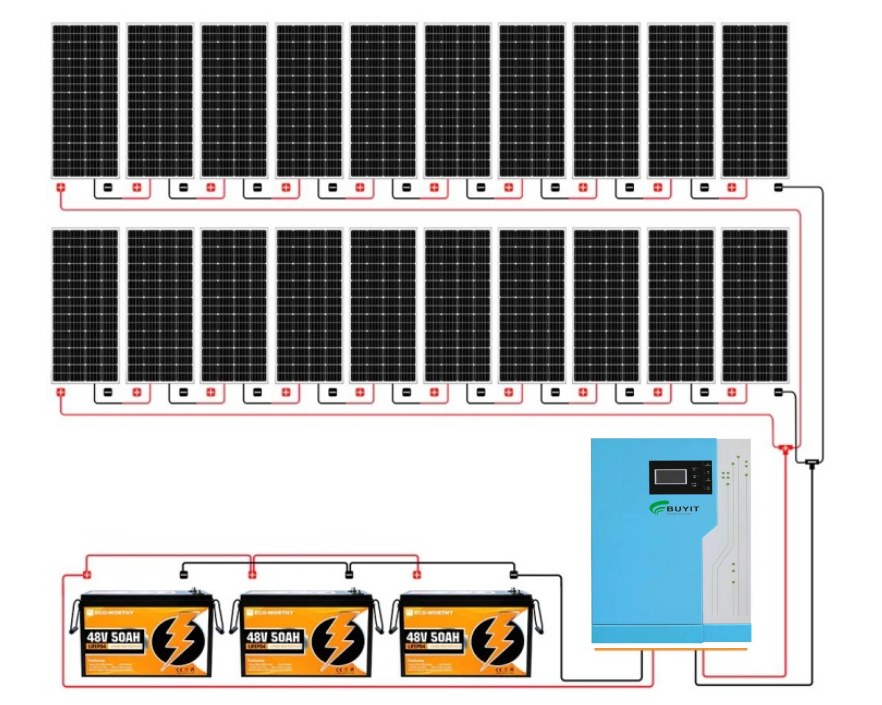
Off-grid inverter, the key equipment of photovoltaic energy storage system
In the photovoltaic off-grid system, the main function of the inverter is to invert the DC power of the battery into AC power. Inverters are often used in off-grid systems, the input is connected to the photovoltaic controller and the battery, and the output is loaded. Off-grid systems are widely used, and inverters come in various forms. According to the output waveform, it is divided into modified wave inverter and sine wave inverter; according to the electrical isolation method, it is divided into high frequency sine wave inverter and power frequency sine wave inverter; the controller and inverter are designed separately, Separate wiring is called split type; combining the controller and inverter is called all-in-one machine, also called inverse control all-in-one machine.
Correction and sine waves
There are two main types of inverter output waveforms, one is sine wave and the other is correction wave. The modified sine wave inverter uses PWM pulse width modulation to generate modified wave output. Due to the harmonic distortion of about 20%, it cannot be used with inductive loads such as air conditioners, but it can be used with resistive loads such as lamps. The modified sine wave inverter adopts a non-isolated coupling circuit with simple components and high efficiency. The pure sine wave inverter adopts the isolation coupling circuit design, the circuit is more complicated and the cost is higher, and it can be connected to any common electrical equipment (including TVs, LCD monitors, etc., especially inductive loads such as refrigerators) without interference.
Power frequency isolation and high frequency isolation
The input and output ends of the pure sine wave off-grid inverter are electrically isolated. According to the electrical structure, they are divided into high-frequency isolation and power frequency isolation. The high-frequency isolation transformer is placed at the DC boost end. The high-frequency alternating current of the inverter is boosted by a high-frequency transformer, then rectified into direct current, and finally inverted into power frequency alternating current. The high-frequency inverter uses a small-sized, light-weight high-frequency magnetic core material, which can reduce The weight of the inverter reduces the volume of the inverter and improves the efficiency of the inverter, but the circuit is more complicated. The power frequency isolation transformer is placed at the AC end, the inverter circuit is relatively simple, and the impact resistance is strong, but the volume is relatively large and the weight is relatively heavy.
- OFF GRID INVERTER14 products
- OFF+ON GRID INVERTER9 products
- DC FAST charging station9 products
- Charging controller2 products
- Lithium battery5 products
- Solar panels2 products
- 110/120VAC Solar Inverter2 products
- Stock in EU warehouse, delivery 3-7 days to EU3 products
- Transformer2 products
- Online UPS1 product
- water pump inverter2 products
- Solar Accessories5 products
- Uncategorized1 product
split and integrated
Since the off-grid system has an extra battery, it is necessary to configure a controller for the components to charge the battery. The controller and the inverter are separated to form two devices, which is the split type. Integrating the controller and the inverter is an integrated type, also known as an integrated control and inverter type. In the split system, the controller and inverter can be selected separately, but the wiring is more complicated, and it is suitable for systems with a relatively large power difference between components and inverters, and systems with large system power. The control and inverter integrated system has a simple structure and convenient wiring for users, and is suitable for systems with relatively small power differences between components and inverters.

When choosing an off-grid inverter, in addition to paying attention to the output waveform and isolation type of the inverter, several technical parameters are also very important, such as system voltage, output power, peak power, conversion efficiency, switching time, etc. The selection of these parameters has a great influence on the power demand of the load.
1) System voltage: It is the voltage of the battery pack. The input voltage of the off-grid inverter is consistent with the output voltage of the controller. When designing and selecting, pay attention to keeping it consistent with the controller.
2) Output power: There are two expressions for the output power of the off-grid inverter. One is the apparent power representation, and the unit is VA. This is a reference to the UPS mark. The actual output active power needs to be multiplied by the power factor, such as 500VA The power factor of the off-grid inverter is 0.8, and the actual output active power is 400W, that is to say, it can drive 400W resistive loads, such as lamps, induction cookers, etc.; the second is the representation of active power, and the unit is W, such as 5000W off-grid inverter, the actual output active power is 5000W.
3) Peak power: In the photovoltaic off-grid system, components, batteries, inverters, and loads constitute the electrical system. The output power of the inverter is determined by the load. Some inductive loads, such as air conditioners, water pumps, etc., inside For electric motors, the starting power is 3-5 times the rated power, so the off-grid inverter has special requirements for overload. The peak power is the overload capacity of the off-grid inverter.
The inverter provides the load with starting energy, part of which comes from the battery or photovoltaic modules, and the excess part is provided by the energy storage elements inside the inverter—capacitors and inductors. Capacitors and inductors are both energy storage components. The difference is that capacitors store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. The larger the capacity of the capacitor, the more electricity it stores. An inductor stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. The greater the permeability of the inductor core, the greater the inductance, and the more energy it can store.
4) Conversion efficiency: The conversion efficiency of the off-grid system includes two aspects. One is the efficiency of the machine itself. The circuit of the off-grid inverter is complex and needs to undergo multi-level conversion, so the overall efficiency is slightly lower than that of the grid-connected inverter, generally at 80 Between -90%, the higher the power of the inverter, the higher the efficiency, the higher the efficiency of high-frequency isolation than the power frequency isolation, and the higher the system voltage, the higher the efficiency. The second is the charging and discharging efficiency of the battery. This is related to the type of the battery. When the photovoltaic power generation is synchronized with the load power consumption, the photovoltaic power can be directly supplied to the load without battery conversion.
5) Switching time: The off-grid system has loads and has three modes: photovoltaic, battery, and mains. When the battery energy is insufficient and switches to the mains mode, there is a switching time. Some off-grid inverters use electronic switches to switch. Within 10 milliseconds, the desktop computer won’t shut down and the lights won’t flicker. Some off-grid inverters use relay switching, the time may exceed 20 milliseconds, and the desktop computer may shut down or restart.

Summarize
In terms of cost, the modified wave inverter is the most economical, and the power frequency inverter is the highest; in terms of load capacity, the power frequency inverter has the strongest capability. Therefore, when choosing an inverter, it depends on the application occasion. If it is just a simple lighting application, it is recommended to use a modified wave inverter, which can save the initial cost; High-frequency inverter, with strong load capacity; if it is a comprehensive load, it is recommended to use a high-frequency inverter, taking into account cost and load capacity

-
 1.5kw/2.5kw/3.5kw off grid inverter 230VDC PV: 30-500V
1.5kw/2.5kw/3.5kw off grid inverter 230VDC PV: 30-500V -
 1p 1.5p 2p 3p Inverter Cool & Heat Split Solar Air Conditioner
1p 1.5p 2p 3p Inverter Cool & Heat Split Solar Air Conditioner -
 Wallbox EV Charger Home Use AC Electric Vehicle Charger 7kw 11kw 22kw Portable EV Charging Station
Wallbox EV Charger Home Use AC Electric Vehicle Charger 7kw 11kw 22kw Portable EV Charging Station -
 CTS CCS CHAdeMO GBT Road Rescue DC Fast Charging Station 20KW 60kW Mobile EV charging station with lifepo4 battery
CTS CCS CHAdeMO GBT Road Rescue DC Fast Charging Station 20KW 60kW Mobile EV charging station with lifepo4 battery -
 Energy Charging Pile 60kw 120kw 180kw 240kw DC OCPP App Control Fast Car EV Charger Station
Energy Charging Pile 60kw 120kw 180kw 240kw DC OCPP App Control Fast Car EV Charger Station -
 UL Certified 60kw 90kw 120kw 150kw supercharger EV bus charging station
UL Certified 60kw 90kw 120kw 150kw supercharger EV bus charging station -
 Brushless DC fans for solar inverter 12V 0.4A
Brushless DC fans for solar inverter 12V 0.4A -
 5500W 48V 100A MPPT PV range 60-500V Off Grid Solar Inverter
5500W 48V 100A MPPT PV range 60-500V Off Grid Solar Inverter -
 MC4 Male/Female Solar Panel Cable Connectors
MC4 Male/Female Solar Panel Cable Connectors